Treatment
Herpes Explained
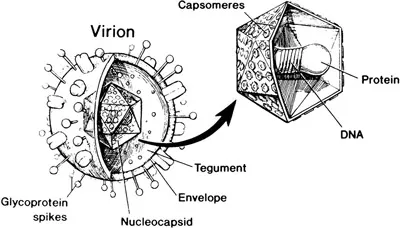
What is herpes?
Herpes is a common group of viral infections that are caused by the Herpes virus. There are many different types of herpes viruses including the Varicella Zoster virus which causes chickenpox and shingles and the Epstein Barr virus which causes glandular fever. The most common type of Herpes virus is called the Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV).
There are two types of Herpes Simplex Virus: HSV-1 and HSV-2. In the past, it was thought that HSV-1 was responsible for oral herpes and HSV-2 for genital herpes. However, we now know that this is not true and both types of the virus can cause oral or genital symptoms. The two forms are genetically different but produce similar symptoms. The main difference is that when HSV-1 affects the genitals it does not commonly recur whereas when HSV-2 affects the genitals it is far more likely to recur.
Infection with the herpes simplex virus is extremely common. It is thought that up to 6 in 10 people carry HSV-1 and 1 in 10 people carry HSV-2. The majority of carriers have no symptoms and do not know that they carry the virus.
How is herpes simplex transmitted?
Both forms of herpes simplex are highly contagious and are transmitted via direct skin to skin contact with someone who carries the herpes simplex virus, even if they do not have symptoms.
Genital Herpes:
Transmitted via sexual contact (vaginal, anal and oral).
Oral Herpes:
Transmitted via close personal contact, most commonly via kissing.
The virus is carried in bodily fluid and can enter the skin via a break in the skin such as a cut or scratch but more commonly enters via mucosal membranes such as the mouth or genital area. When the virus enters the skin, it replicates before being transported to nerve roots where it remains latent (inactive). When the virus is inactive, it cannot be transmitted to another person. The virus is most commonly transmitted when the virus is in the active stage and showing symptoms, however it can be transmitted via the shedding stage of the virus and often there are no symptoms at this stage.
What are the symptoms of herpes?
Genital Herpes:
The first outbreak usually occurs 1-2 weeks after sexual contact and exposure to the virus. Usually general discomfort is felt in the area where the virus occurs and the most common symptoms are itching, soreness and a tingling sensation in the genital area. Red bumps appear that develop into blisters which over a period of a few weeks can develop into painful sores which crust over before healing. The initial outbreak is sometimes associated with other symptoms such as fever, headache, muscle ache and other flu-like symptoms. The initial episode usually lasts 2-3 weeks and is often the worst.
Recurring outbreaks are usually a lot milder and shorter, often only lasting for 3 days. Symptoms include minor itching and often outbreaks are asymptomatic. The number of recurrent outbreaks a person suffers from widely varies and is dependant on the individual themselves. Generally in the first year of infection, there is an average of four outbreaks and this decreases with each year.
Oral Herpes:
Most adults have no symptoms with the first outbreak, but when they do occur it can be quite painful. Symptoms include sore throat, bad breath and sores that can develop into ulcers on the lips and sometimes on the tongue. After the primary episode, symptoms are usually limited to cold sores that develop on the lips. These can sometimes affect other parts of the face although this is rare. There are a number of different triggers for outbreaks but common factors include stress, exposure to UV light from the sun, alcohol intake, tiredness and fatigue.
How do I treat herpes?
Genital Herpes:
There is no cure to completely eradicate the herpes virus from the body. It is a long term condition that lays dormant in the body until the virus is reactivated and an outbreak occurs. Treatment is therefore aimed at reducing the number of outbreaks as well as reducing symptoms during an outbreak. The two most commonly used medications are Aciclovir and Valaciclovir, both of which are antivirals. They work by reducing the viral load hence controlling outbreaks by reducing the severity and duration of symptoms. They also can be taken on a daily basis to suppress the virus and this is suitable for patients who have frequent outbreaks, i.e. greater than 6 per year. Valaciclovir has a longer duration of action compared to Aciclovir and so does not need to be taken as frequently.
Taking simple analgesics like Paracetamol or Ibuprofen will help to reduce the fever and muscle ache that can sometimes occur with the first outbreak. Furthermore, simple measures such as maintaining excellent hygiene, wearing cotton underwear and loose trousers will help to reduce the discomfort as well as duration of symptoms. Many patients find having lukewarm baths and placing an ice pack on the affected area can give a lot of relief for the itching and tingling sensation that can occur during an outbreak.
Oral Herpes:
The most commonly used medication to treat cold sores is Aciclovir 5% cream which can be bought over the counter in pharmacies. This should be used five times a day for five days at the first signs of an outbreak for maximum effectiveness. It can shorten the duration as well as reducing the severity of symptoms if used correctly. In more severe cases, antiviral tablets such as aciclovir or valaciclovir may be prescribed.